Create an SQS queue service
🎯 Goal: Craft a ready-to-use AWS SQS queue service specification—complete with schema, UI, and IaC—so your teams can consistently provision queues in your platform.
Introduction
In this guide you’ll model a reusable service specification that provisions an AWS SQS queue. You’ll design the JSON Schema (what’s configurable), optionally add a UI Schema (layout & hints), and finally copy the IaC that the playground generates so teams can roll this out with Terraform/OpenTofu or the CLI. You’ll also create a link specification for the service, so it can be triggered from other entities in your platform.
What you’ll set up
By the end of this guide, you'll have:
- A service specification for SQS queues with sensible defaults
- An optional UI Schema that groups advanced options
- A copy‑pastable Terraform/OpenTofu snippet (or CLI) from the playground
- A link specification wired to your service
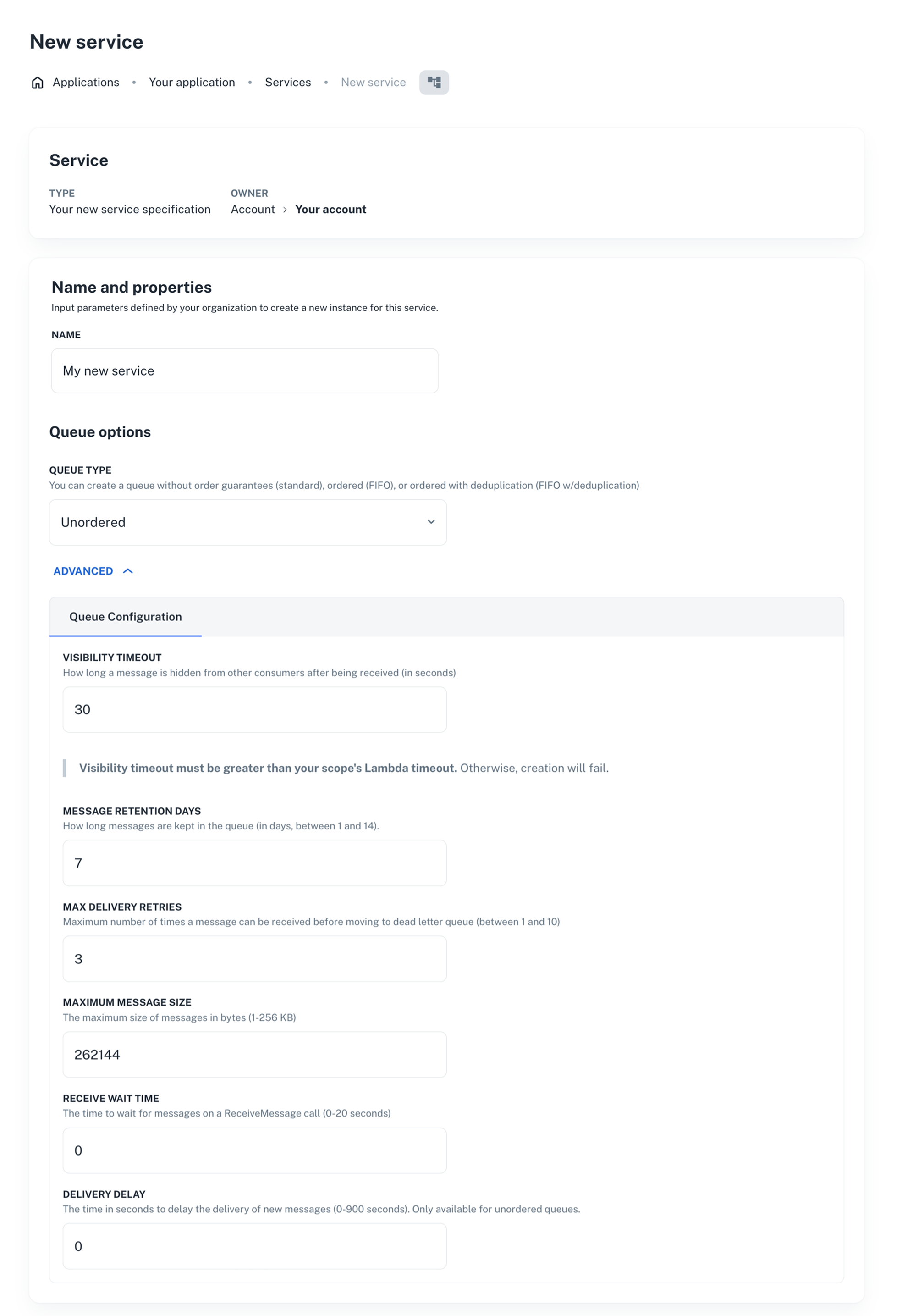
This is how the SQS queue service will look like for developers:
Prerequisites
You’ll need:
- Terraform/OpenTofu
- A nullplatform API key with the Ops role assigned (recommended at the organization level)
- If you're planning to use the nullplatform CLI instead of Terraform/OpenTofu, the nullplatform CLI installed:
curl https://cli.nullplatform.com/install.sh | sh
1. Open the service specification playground
- Go to Platform settings > Services > Specifications.
- Click + New service specification. The playground opens with three tabs: Specification data, Schema, and UI schema.
The playground also includes Terraform/OpenTofu and CLI tabs that render ready‑to‑use snippets from your schema.
💡 Tip: You can also open an existing spec to iterate on it. Preview updates live in the right‑hand panel.
2. Fill in specification data (name, visibility, defaults)
In Specification data, define general settings for the service (name, visibility, dimensions, default actions).
Default template shown in the UI:
{
"name": "My new service specification",
"visible_to": [
"organization=<your-organization-id>"
],
"type": "dependency",
"use_default_actions": true,
"dimensions": {},
"assignable_to": "any",
"attributes": {
"values": {}
}
}
Key fields
-
visible_to lets you limit where the service is available by specifying which NRNs can access it (org, account, namespace, or application). Example for a specific application:
["organization=1:account=2:namespace=3:application=4"]💡 Tip: We recommend keeping a wildcard at the namespace level so the service remains visible to app‑level users too. If you don’t set it this way, developers who only have application‑level permissions might not see the service.
Like this:
["organization=1:account=2:namespace=*"] -
assignable_to lets you control where instances can be attached. Keep
anyunless you need to constrain it (e.g., only by dimension"assignable_to": "dimension").
3. Add the SQS Schema
Switch to Schema and paste the example below. You’ll see the form update in the Preview panel in real time.
💡 Tip: Tweak defaults and limits to match your org’s guardrails.
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#",
"type": "object",
"title": "SQS Queue Configuration",
"description": "Essential configuration for an AWS SQS Queue",
"properties": {
"queue_type": {
"type": "string",
"oneOf": [
{
"const": "standard",
"title": "Unordered"
},
{
"const": "fifo",
"title": "Ordered (FIFO)"
},
{
"const": "fifo_with_deduplication",
"title": "Ordered (FIFO) with content-based deduplication"
}
],
"title": "Queue Type",
"default": "standard",
"description": "Create a queue without order guarantees (standard), ordered (FIFO), or ordered with deduplication (FIFO with content-based deduplication).",
"editableOn": ["create"]
},
"queue_arn": {
"type": "string",
"readOnly": true,
"visibleOn": ["read", "update"]
},
"max_message_size": {
"type": "integer",
"title": "Maximum Message Size",
"default": 262144,
"maximum": 262144,
"minimum": 1024,
"description": "The maximum size of messages in bytes (1024 bytes – 262144 bytes)"
},
"visibility_timeout": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "How long a message is hidden from other consumers after being received (in seconds)",
"minimum": 0,
"maximum": 43200,
"placeholder": 30,
"default": 30,
"examples": [30, 60, 300, 900]
},
"message_retention_days": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "How long messages are kept in the queue (in days, between 1 and 14).",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 14,
"placeholder": 7,
"default": 7
},
"receive_wait_time_seconds": {
"type": "integer",
"title": "Receive Wait Time",
"default": 0,
"maximum": 20,
"minimum": 0,
"description": "The time to wait for messages on a ReceiveMessage call (0-20 seconds)"
},
"delay_seconds": {
"type": "integer",
"title": "Delivery Delay",
"default": 0,
"maximum": 900,
"minimum": 0,
"description": "The time in seconds to delay the delivery of new messages (0-900 seconds). Only available for unordered queues."
},
"max_delivery_retries": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Maximum number of times a message can be received before moving to dead letter queue (between 1 and 10)",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 10,
"placeholder": 3,
"default": 3,
"examples": [1, 3, 5, 10]
},
"enable_dlq": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether to create a dead-letter queue for failed messages",
"default": true
},
"dead_letter_arn": {
"type": "string",
"description": "ARN of the created DLQ (available when the DLQ option is set to true)",
"export": true,
"pattern": "^arn:aws:sqs:[a-z0-9-]+:[0-9]+:([a-zA-Z0-9_-]+\\.fifo|[a-zA-Z0-9_-]+)$",
"visibleOn": ["read"],
"editableOn": []
},
"fifoQueue": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether this should be a FIFO queue (guarantees order and exactly-once delivery)",
"default": false
}
},
"required": [],
"additionalProperties": false
}
Special keys used in the schema
-
visible_on: defined the visibility of properties based on the lifecycle of the instance (e.g.,
["create", "read"]). -
editable_on: control when a property can be edited, based on the lifecycle of the instance (e.g.,
["create"]).
4. (Optional) Design the UI Schema
Open UI schema and paste the example below to customize layout and add helpful hints. This step is optional if you want a more guided form experience, or skip it if the default layout works for your team.
{
"type": "VerticalLayout",
"elements": [
{
"text": "### Queue options",
"type": "Label",
"options": {
"format": "markdown"
}
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/queue_type"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/queue_arn"
},
{
"type": "Categorization",
"options": {
"collapsable": {
"label": "ADVANCED",
"collapsed": true
}
},
"elements": [
{
"type": "Category",
"label": "Queue Configuration",
"elements": [
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/visibility_timeout"
},
{
"text": "> **Visibility timeout must be greater than your scope's Lambda timeout.** Otherwise, creation will fail.",
"type": "Label",
"options": {
"format": "markdown"
}
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/message_retention_days"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/max_delivery_retries"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/max_message_size"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/receive_wait_time_seconds"
},
{
"rule": {
"effect": "HIDE",
"condition": {
"scope": "#/properties/queue_type",
"schema": {
"enum": [
"fifo",
"fifo_with_deduplication"
]
}
}
},
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/delay_seconds"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
✅ Checkpoint
Confirm the preview shows the basic fields plus an ADVANCED group. Changing Queue Type to FIFO should automatically hide the Delivery Delay field.
5. Copy the generated IaC
Once your spec looks good, open the Terraform/OpenTofu tab (or CLI tab) in the playground. Copy the rendered resources into your infrastructure repo and apply as usual. The playground keeps the IaC in sync with your schema edits.
- IaC
- CLI
terraform {
required_providers {
nullplatform = {
source = "nullplatform/nullplatform"
}
}
}
provider "nullplatform" {}
resource "nullplatform_service_specification" "my_new_service_specification" {
name = "My new service specification"
type = "dependency"
assignable_to = "any"
use_default_actions = true
visible_to = [
"<your-specified-NRN>"
]
dimensions = jsonencode({})
attributes = jsonencode({
"values": {},
"schema": {
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#",
"type": "object",
"title": "SQS Queue Configuration",
"description": "Essential configuration for an AWS SQS Queue",
"properties": {
"queue_type": {
"type": "string",
"oneOf": [
{
"const": "standard",
"title": "Unordered"
},
{
"const": "fifo",
"title": "Ordered (FIFO)"
},
{
"const": "fifo_with_deduplication",
"title": "Ordered (FIFO) with content-based deduplication"
}
],
"title": "Queue Type",
"default": "standard",
"description": "Create a queue without order guarantees (standard), ordered (FIFO), or ordered with deduplication (FIFO with content-based deduplication).",
"editableOn": [
"create"
]
},
"queue_arn": {
"type": "string",
"readOnly": true,
"visibleOn": [
"read",
"update"
]
},
"max_message_size": {
"type": "integer",
"title": "Maximum Message Size",
"default": 262144,
"maximum": 262144,
"minimum": 1024,
"description": "The maximum size of messages in bytes (1-256 KB)"
},
"visibility_timeout": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "How long a message is hidden from other consumers after being received (in seconds)",
"minimum": 0,
"maximum": 43200,
"placeholder": 30,
"default": 30,
"examples": [
30,
60,
300,
900
]
},
"message_retention_days": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "How long messages are kept in the queue (in days, between 1 and 14).",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 14,
"placeholder": 7,
"default": 7
},
"receive_wait_time_seconds": {
"type": "integer",
"title": "Receive Wait Time",
"default": 0,
"maximum": 20,
"minimum": 0,
"description": "The time to wait for messages on a ReceiveMessage call (0-20 seconds)"
},
"delay_seconds": {
"type": "integer",
"title": "Delivery Delay",
"default": 0,
"maximum": 900,
"minimum": 0,
"description": "The time in seconds to delay the delivery of new messages (0-900 seconds). Only available for unordered queues."
},
"max_delivery_retries": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Maximum number of times a message can be received before moving to dead letter queue (between 1 and 10)",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 10,
"placeholder": 3,
"default": 3,
"examples": [
1,
3,
5,
10
]
},
"enable_dlq": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether to create a dead-letter queue for failed messages",
"default": true
},
"dead_letter_arn": {
"type": "string",
"description": "ARN of the created DLQ (available when the DLQ option is set to true)",
"export": true,
"pattern": "^arn:aws:sqs:[a-z0-9-]+:[0-9]+:([a-zA-Z0-9_-]+\\.fifo|[a-zA-Z0-9_-]+)$",
"visibleOn": [
"read"
],
"editableOn": []
},
"fifoQueue": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether this should be a FIFO queue (guarantees order and exactly-once delivery)",
"default": false
}
},
"required": [],
"additionalProperties": false,
"uiSchema": {
"type": "VerticalLayout",
"elements": [
{
"text": "### Queue options",
"type": "Label",
"options": {
"format": "markdown"
}
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/queue_type"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/queue_arn"
},
{
"type": "Categorization",
"options": {
"collapsable": {
"label": "ADVANCED",
"collapsed": true
}
},
"elements": [
{
"type": "Category",
"label": "Queue Configuration",
"elements": [
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/visibility_timeout"
},
{
"text": "> **Visibility timeout has to be higher than your scope's lambda timeout.** Failing to meet this condition will make the service creation to fail. You can check your lambda's timeout from the \"Scopes\" section in the sidebar.",
"type": "Label",
"options": {
"format": "markdown"
}
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/message_retention_days"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/max_delivery_retries"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/max_message_size"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/receive_wait_time_seconds"
},
{
"rule": {
"effect": "HIDE",
"condition": {
"scope": "#/properties/queue_type",
"schema": {
"enum": [
"fifo",
"fifo_with_deduplication"
]
}
}
},
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/delay_seconds"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
}
})
}
np service specification create --body '{
"name": "My new service specification",
"visible_to": [
"organization=<your-organization-id>"
],
"use_default_actions": true,
"dimensions": {},
"assignable_to": "any",
"attributes": {
"values": {},
"schema": {
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#",
"type": "object",
"title": "SQS Queue Configuration",
"description": "Essential configuration for an AWS SQS Queue",
"properties": {
"queue_type": {
"type": "string",
"oneOf": [
{
"const": "standard",
"title": "Unordered"
},
{
"const": "fifo",
"title": "Ordered (FIFO)"
},
{
"const": "fifo_with_deduplication",
"title": "Ordered (FIFO) with content-based deduplication"
}
],
"title": "Queue Type",
"default": "standard",
"description": "Create a queue without order guarantees (standard), ordered (FIFO), or ordered with deduplication (FIFO with content-based deduplication).",
"editableOn": [
"create"
]
},
"queue_arn": {
"type": "string",
"readOnly": true,
"visibleOn": [
"read",
"update"
]
},
"max_message_size": {
"type": "integer",
"title": "Maximum Message Size",
"default": 262144,
"maximum": 262144,
"minimum": 1024,
"description": "The maximum size of messages in bytes (1-256 KB)"
},
"visibility_timeout": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "How long a message is hidden from other consumers after being received (in seconds)",
"minimum": 0,
"maximum": 43200,
"placeholder": 30,
"default": 30,
"examples": [
30,
60,
300,
900
]
},
"message_retention_days": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "How long messages are kept in the queue (in days, between 1 and 14).",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 14,
"placeholder": 7,
"default": 7
},
"receive_wait_time_seconds": {
"type": "integer",
"title": "Receive Wait Time",
"default": 0,
"maximum": 20,
"minimum": 0,
"description": "The time to wait for messages on a ReceiveMessage call (0-20 seconds)"
},
"delay_seconds": {
"type": "integer",
"title": "Delivery Delay",
"default": 0,
"maximum": 900,
"minimum": 0,
"description": "The time in seconds to delay the delivery of new messages (0-900 seconds). Only available for unordered queues."
},
"max_delivery_retries": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Maximum number of times a message can be received before moving to dead letter queue (between 1 and 10)",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 10,
"placeholder": 3,
"default": 3,
"examples": [
1,
3,
5,
10
]
},
"enable_dlq": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether to create a dead-letter queue for failed messages",
"default": true
},
"dead_letter_arn": {
"type": "string",
"description": "ARN of the created DLQ (available when the DLQ option is set to true)",
"export": true,
"pattern": "^arn:aws:sqs:[a-z0-9-]+:[0-9]+:([a-zA-Z0-9_-]+\\.fifo|[a-zA-Z0-9_-]+)$",
"visibleOn": [
"read"
],
"editableOn": []
},
"fifoQueue": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether this should be a FIFO queue (guarantees order and exactly-once delivery)",
"default": false
}
},
"required": [],
"additionalProperties": false,
"uiSchema": {
"type": "VerticalLayout",
"elements": [
{
"text": "### Queue options",
"type": "Label",
"options": {
"format": "markdown"
}
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/queue_type"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/queue_arn"
},
{
"type": "Categorization",
"options": {
"collapsable": {
"label": "ADVANCED",
"collapsed": true
}
},
"elements": [
{
"type": "Category",
"label": "Queue Configuration",
"elements": [
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/visibility_timeout"
},
{
"text": "> **Visibility timeout must be greater than your scope's Lambda timeout.** Otherwise, creation will fail.",
"type": "Label",
"options": {
"format": "markdown"
}
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/message_retention_days"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/max_delivery_retries"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/max_message_size"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/receive_wait_time_seconds"
},
{
"rule": {
"effect": "HIDE",
"condition": {
"scope": "#/properties/queue_type",
"schema": {
"enum": [
"fifo",
"fifo_with_deduplication"
]
}
}
},
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/delay_seconds"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
}'
✅ Checkpoint
Verify that your new service specification appears under Platform settings > Services > Specifications.
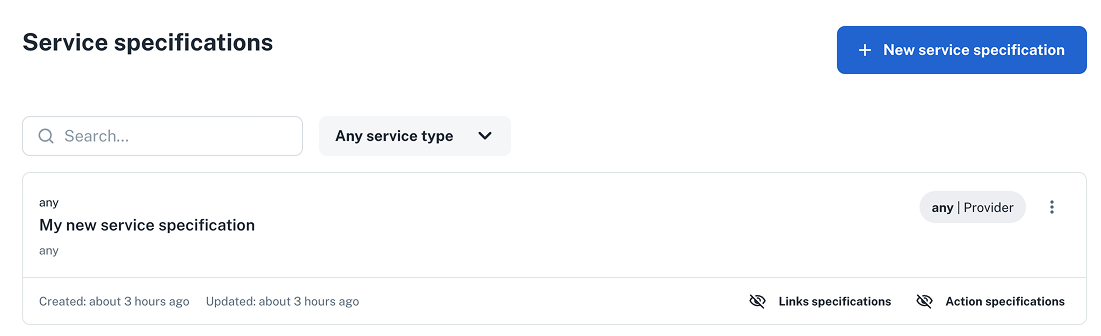
6. Create a link specification
Now that the service spec is created (with standard actions), create a link specification for the service so it can be invoked from scopes or other services.
As with service specs, you can craft link specs using the playground: open the service spec you created above and click + New link specification.
For this guide, we’ll define a minimal link spec using only Specification data (name and defaults). You can tweak or extend it later with a custom schema.
{
"name": "My new link specification",
"unique": false,
"use_default_actions": true,
"results": {
"schema": {
"type": "object",
"required": [],
"properties": {}
},
"values": {}
},
"attributes": {}
}
7. Copy the generated IaC (link)
As with services, open the Terraform/OpenTofu tab (or CLI tab) in the playground. Copy the rendered resources into your infrastructure repo and apply as usual. The playground keeps the IaC in sync with your schema edits.
- IaC
- CLI
terraform {
required_providers {
nullplatform = {
source = "nullplatform/nullplatform"
}
}
}
provider "nullplatform" {}
resource "nullplatform_link_specification" "my_new_link_specification" {
name = "My new link specification"
type = ""
service_specification_id = ""
retryable = false
use_default_actions = true
attributes = jsonencode({
"schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"message": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"message"
],
"uiSchema": {}
}
})
results = jsonencode({
"schema": {
"type": "object",
"required": [],
"properties": {}
},
"values": {}
})
}
np link-specification create --body '{
"name": "My new link specification",
"unique": false,
"use_default_actions": true,
"results": {
"schema": {
"type": "object",
"required": [],
"properties": {}
},
"values": {}
},
"attributes": {
"schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"message": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"message"
],
"uiSchema": {}
}
}
}'
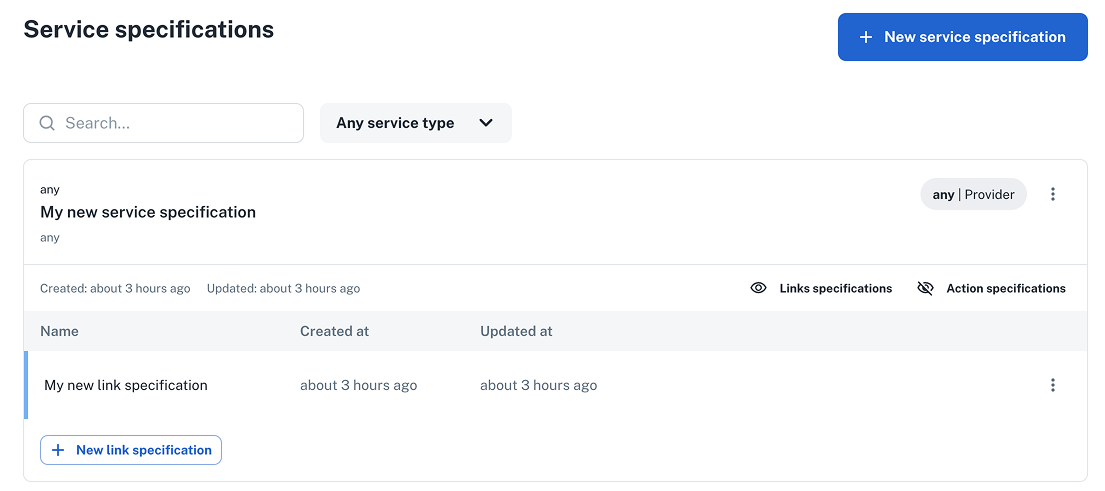
✅ Checkpoint
Verify that your new link specification is wired to the service spec and appears under Platform settings > Services > Specifications.
Wrap-up 🎉
You’ve built a reusable SQS service with a clean UI, validated inputs, and ready-to-use IaC, plus a link specification so it can be triggered from other entities.
This ensures teams can provision queues quickly and consistently, with your organization’s defaults and guardrails baked in
Related docs
Quick links to resources used in this guide: