Integrate Datadog logs, APM, and custom metrics
Nullplatform supports Datadog as a logs, APM, and metrics provider. This guide walks you through enabling the integration, configuring your scopes, and exposing metrics in your Datadog account.
Grant nullplatform access to Datadog
You can enable Datadog for the following scope types:
- Instance-based
- Kubernetes-based
Instance-based scopes
To configure Datadog for instance-based scopes:
- Log in to your organization's portal at
https://<your-org-name>.app.nullplatform.io. - Go to Platform settings > Metrics/Logging.
- Click + New configuration and select Datadog as the provider.
- Fill in the required configuration details.
- Click Create configuration to save your setup.
See the Supported integrations and Providers docs for more details.
Kubernetes-based scopes
To enable Datadog for your Kubernetes-based scopes:
For Kubernetes-based scopes, you’ll need to create a Kubernetes secret with your Datadog API key:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: datadog-secret
namespace: nullplatform-tools
type: Opaque
data:
DATADOG_API_KEY: <your key>
Then, update the env section of the nullplatform-log-controller container in your null-metrics configuration:
env:
- name: DATADOG_LOGS_ENABLED
value: 'true'
- name: DATADOG_PERFORMANCE_METRICS_ENABLED
value: 'true'
- name: DATADOG_API_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: datadog-secret
key: DATADOG_API_KEY
Enable logs and metrics when creating scopes
Once Datadog access is granted through providers, configure scopes to use Datadog for logs and metrics:
- Go to Development > Scopes, and click + New scope.
- Complete the basic information (environment, country, name).
- Under Target, select Server instances or Kubernetes.
- Expand Advanced > Logs/Metrics and choose Datadog as the provider.
- Click Create scope.
Create custom tags
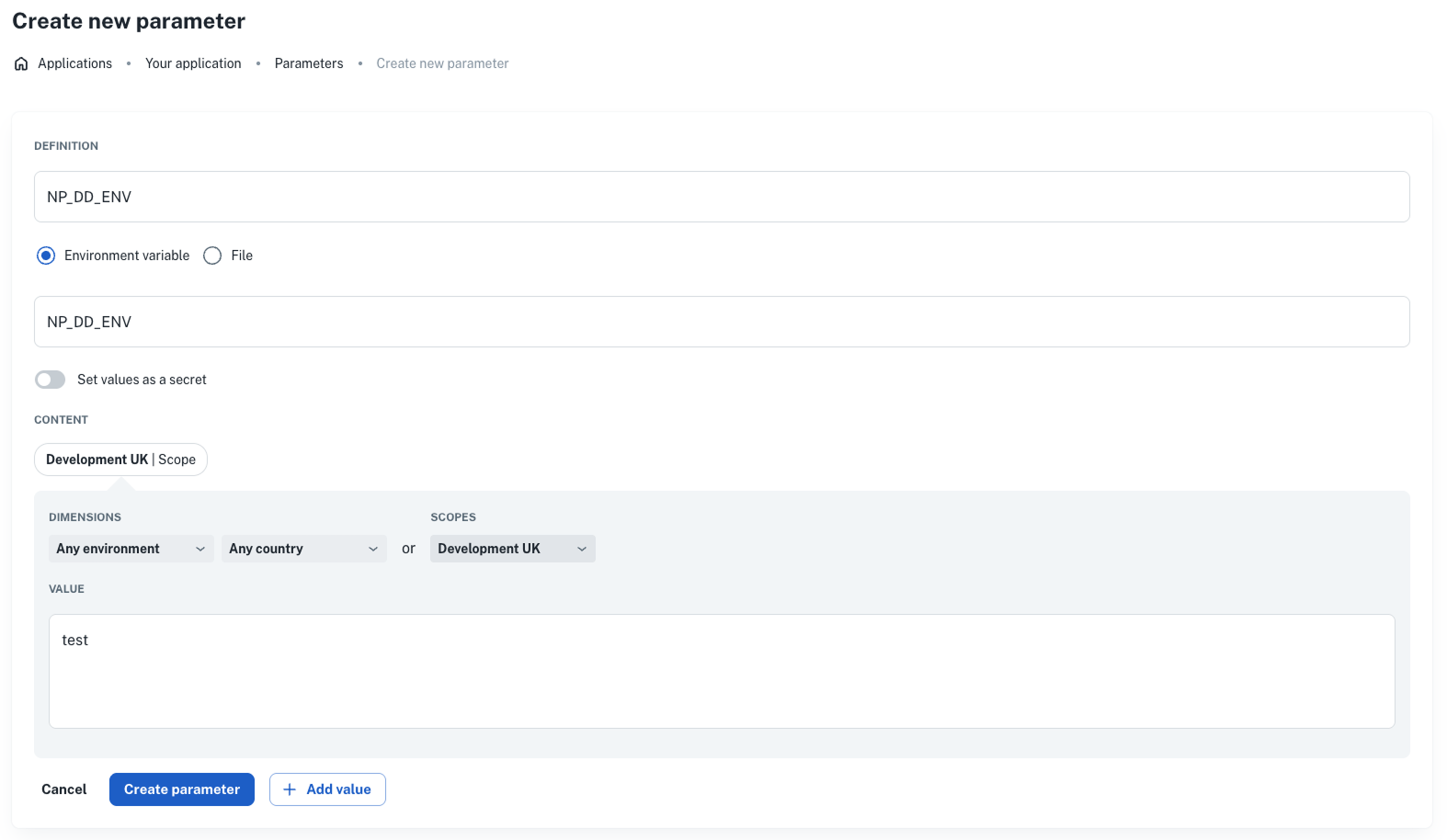
To send custom tags from nullplatform to Datadog, define environment variables with the format NP_DD_<tag-name>.
Example:
NP_DD_ENV=test
To create custom tags:
- Go to Development > Parameters and click + New parameter.
- Set:
- Name:
NP_DD_<tag-name>(e.g.,NP_DD_ENV) - Type: Environment variable
- Scope: Choose the scope
- Value: Tag value (e.g.,
test)
- Name:
- Click Create parameter.
Your tag will appear in your Datadog logs as env:test once data starts streaming.
Configure metrics in your Datadog account
Once nullplatform is configured to use Datadog, you must tell Datadog to expose metrics derived from logs. This step is necessary because nullplatform sends metrics as logs, and Datadog must be instructed to generate metrics from them.
1. Access log-based metrics
In Datadog, navigate to Logs > Generate Metrics from the sidebar.
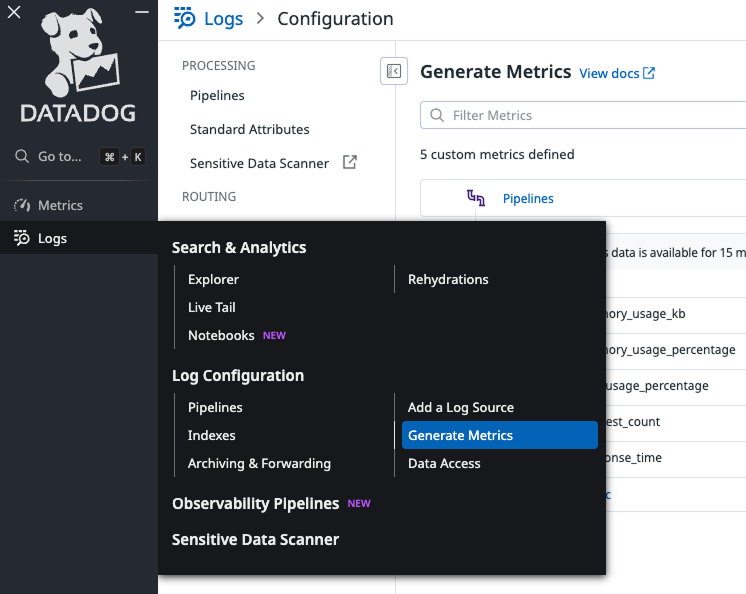
2. Generate metrics
Once you’ve accessed Logs > Generate Metrics, you can define new metrics from your logs. Each metric you configure includes settings similar to the following:
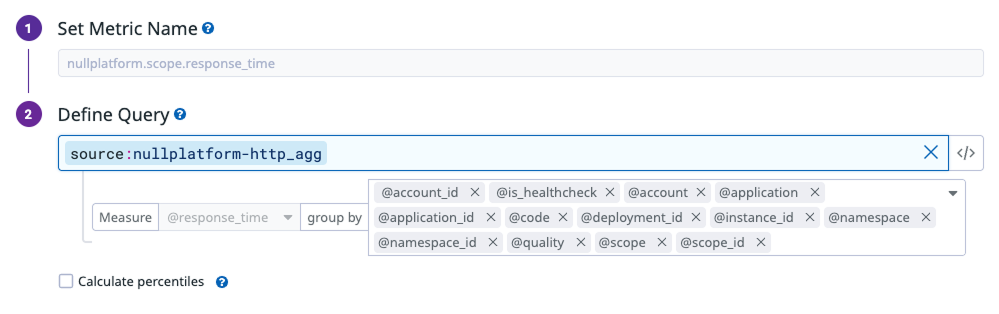
Follow these steps:
-
Click + New Metric to open the configuration panel.
-
Set Metric Name: Enter your metric name, for example:
nullplatform.scope.response_time -
Define Query: Specify the log source (index) that contains the data for this metric.
For example:source:nullplatform-http_agg -
Add the measure attribute: By default, the aggregation type will show as count, which counts log entries.
To change it to a measure:
- Click the dropdown arrow (▾) next to count.
- Add the attribute you want to measure, for example
@response_time, and click Add option. - Once selected, the label should change from count to measure, confirming that Datadog will now use that numeric attribute as the metric value.
-
Group by fields (tags)
Under group by, add the log paths you need to use as tags. These define how your metric is broken down in Datadog dashboards. For example, fornullplatform.scope.response_time, add:@account@account_id@namespace@namespace_id@application
@application_id@scope@scope_id@deployment_id
@instance_id@code@is_healthcheck@quality -
Preview and create: Review the preview section and click Create Metric.
-
Repeat the process to create these metrics:
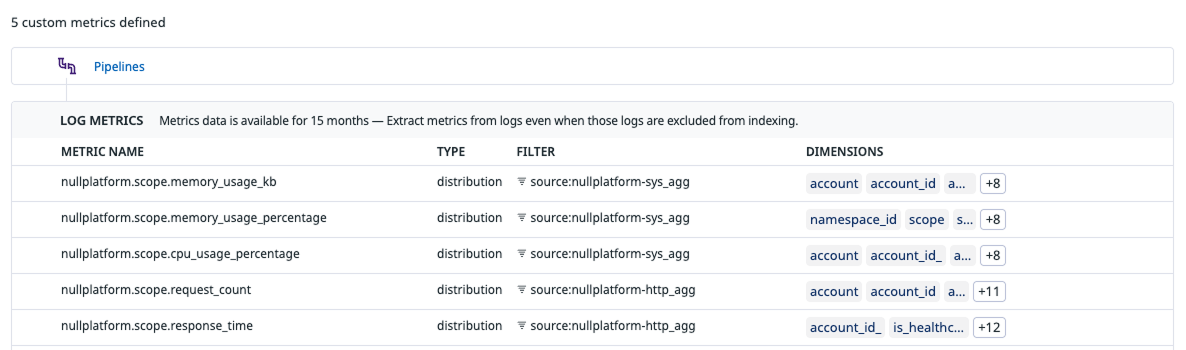
| Metric name | Source (Log Index) | Measure | Tags (Paths) |
|---|---|---|---|
nullplatform.scope.response_time | nullplatform-http_agg | @response_time | @account @account_id @namespace @namespace_id @application @application_id @scope @scope_id @deployment_id @instance_id @code @is_healthcheck @quality |
nullplatform.scope.request_count | nullplatform-http_agg | @counter | @account @account_id @namespace @namespace_id @application @application_id @scope @scope_id @deployment_id @instance_id @code @is_healthcheck @quality |
nullplatform.scope.cpu_usage_percentage | nullplatform-sys_agg | @cpu_usage_percentage | @account @account_id @namespace @namespace_id @application @application_id @scope @scope_id @deployment_id @instance_id |
nullplatform.scope.memory_usage_percentage | nullplatform-sys_agg | @memory_usage_percentage | @account @account_id @namespace @namespace_id @application @application_id @scope @scope_id @deployment_id @instance_id |
nullplatform.scope.memory_usage_kb | nullplatform-sys_agg | @user_memory_kb | @account @account_id @namespace @namespace_id @application @application_id @scope @scope_id @deployment_id @instance_id |
3. Verify configuration
Once you’ve created the metrics, your Datadog account should display them similarly to the following:
You can now view your nullplatform metrics directly in Datadog dashboards or in the Performance section of your nullplatform UI.
Send custom metrics and APM data via a proxy agent
To transmit custom metrics and APM data to Datadog, we recommend you configure a Proxy Agent. This setup lets your application send data directly to the agent, minimizing the number of host agents needed and streamlining your architecture.
Here is a diagram of the proposed architecture:
For optimal performance and reliability, we recommend using a Network Load Balancer (NLB) with at least two agents.
Metrics reference
Common group by fields
The following fields are commonly used across multiple metrics:
| Field name | Description |
|---|---|
@account | The account name. |
@account_id | The unique identifier for the account. |
@namespace | The namespace name. |
@namespace_id | The unique identifier for the namespace. |
@application | The application name. |
@application_id | The unique identifier for the application. |
@scope | The scope name. |
@scope_id | The unique identifier for the scope. |
@deployment_id | The unique identifier for the deployment. |
@instance_id | The unique identifier for the instance. |
Additional group by fields
The following fields are used for HTTP metrics:
| Field name | Description |
|---|---|
@quality | The quality of the request (HTTP metrics only). |
@code | The HTTP response code (HTTP metrics only). |
@is_healthcheck | Indicates if the request is a healthcheck (HTTP metrics only). |