Catalog
We’ve rebranded metadata as catalog to better reflect how structured data works across nullplatform.
The catalog feature in nullplatform lets you extend and enrich your entities, like builds, applications, and namespaces—with structured, validated catalogs that power forms, dashboards, and automation across the platform.
With just a few schema definitions, you can:
- Add custom forms to entity creation flows
- Display dynamic catalogs in dashboards (like "Quality Insights" for builds)
- Validate inputs automatically
What is the catalog?
The catalog is a system that brings structure and validation to your platform data. You use it to define custom fields, like "compliance level", "application type", or "test coverage", and attach them to any entity.
These fields are defined using JSON Schema, which means you can:
- Enforce consistent input across teams
- Generate forms automatically
- Control how and where the data appears
It’s:
- Flexible – You decide what catalog is relevant for your team.
- Validated – Every field follows rules you define in the schema.
- Scalable – Specs can be scoped globally or to specific teams using NRNs.
Core building blocks
The catalog is built on two core components:
- Specifications: A JSON Schema that defines what catalog fields an entity can have (and how they behave).
- Instances: A filled-out version of that spec, attached to a specific entity.
Create and edit catalogs directly in the UI
You can now create and manage catalogs entirely from the UI, with no API required for most use cases.
Here’s how it works:
- When you create an entity (like a namespace or application), nullplatform will show an autogenerated form based on your catalog spec.
- After creation, the catalog appears in the entity’s detail view, where users can click "Show all" to review or update values.
💡 This is available for
namespace,application, andbuild. Specs are still defined via API for now.
How it works
Here’s the typical workflow:
-
Define a catalog specification
Use the API to define the schema, what fields should appear and how they should behave. Here's an example of a catalog schema for builds:{
"schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"coverage_percent": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Coverage % for this build",
"visibleOn": ["create", "update", "read", "list"]
},
"technical_debt_minutes": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Time-based tech debt metric",
"visibleOn": ["create", "update", "read"]
},
"complexity": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Code complexity score",
"visibleOn": ["read"]
},
"vulnerabilities": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Known vulnerabilities in this build",
"visibleOn": ["read", "update"]
}
}
}
} -
Create catalog instances (via UI or API)
Users fill out data in the autogenerated form during entity creation. Later, they can update fields from the catalog section in the UI.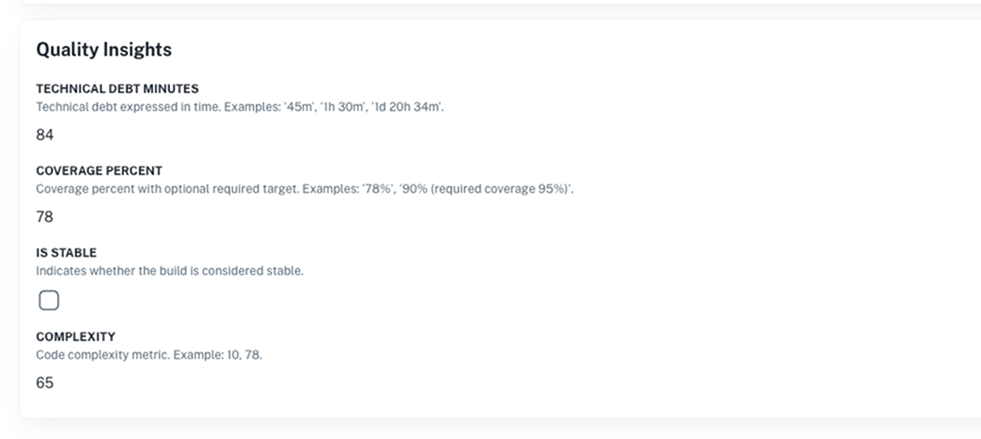
-
Use catalog throughout the platform
The data appears in dashboards (like “Quality Insights” for builds), filters, and policies.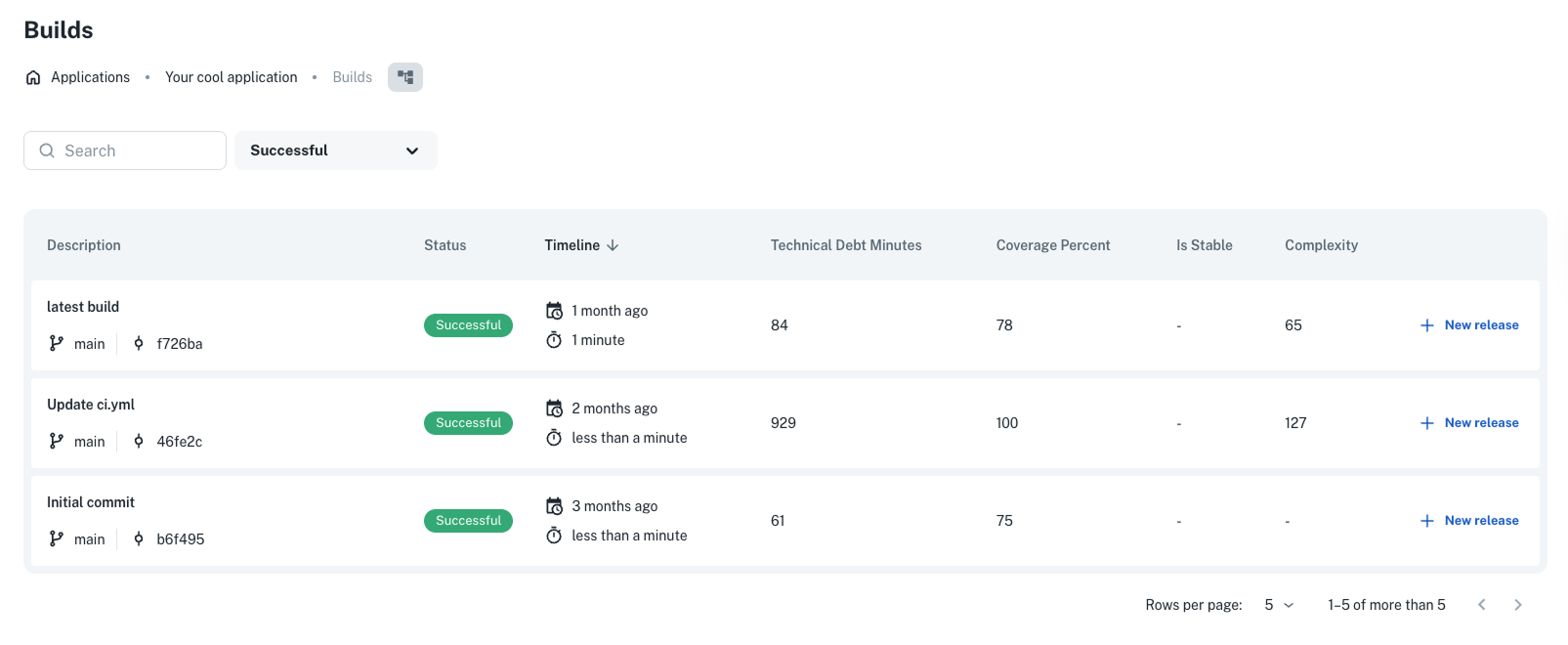
Catalog flow
Next steps
Here’s what to explore next: